The direct removal of silt (desilting) is an important and effective means of eliminating endogenous pollution in the management of rivers and lakes. Contaminated silt, such as that contaminated by industrial wastewater, can cause serious secondary pollution if it is not properly desludged, treated and disposed of. Although the two common methods of dredging river and lake silt are different [1-3], the final treatment is the same: landfill silt, increasing secondary pollution. Due to the inappropriate treatment and disposal of endogenously polluted river and lake silt deposited in polluted water bodies over the years, as well as the lack of understanding of the impact of silt on water quality, many water treatment projects face many difficult practical problems in practice, resulting in unsatisfactory treatment results [4]. In order to efficiently treat river and lake sludge, a new compound chemical process is proposed, which is applied in engineering practice and found that the water content of sludge after dewatering is less than 50%.
1 Compound chemical process for treating river and lake sludge The compound chemical process scheme integrating dredging of sludge, separation of rubbish, sand and gravel, conditioning and coagulation, first flocculation, first concentration, secondary flocculation, secondary concentration, tertiary flocculation, belt filter press dewatering and resource utilisation, etc., is shown in Fig. 1, with pumping of river and lake sludge, and the specific treatment process routes in the dotted box.
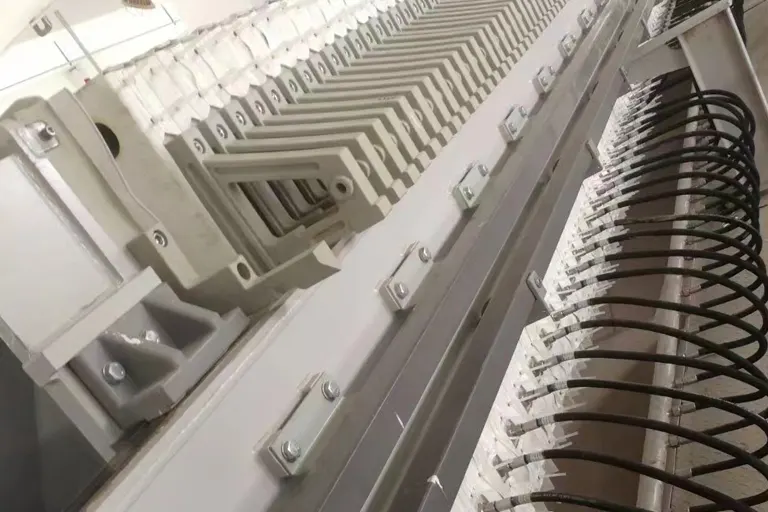
2 Process operation for treating river and lake silt The silt after waste sorting and sand and gravel separation has a small particle size, and because of the large amount of humus and other pollutants, it forms a gelatinous structure that is difficult to dewater under natural conditions. The main function of adding conditioning agent is to break the gel, stabilise the ionic pollutants (e.g. heavy metal ions, etc.), deodorise, coagulate, etc., and form tiny particles. After conditioning, the sludge is coagulated into easy-to-sediment flocs by flocculant net trapping, and the sludge and water are initially separated through a concentration process (by means of a buffer tower). The buffer tower homogenises and buffers the slurry and removes most of the water in the slurry to increase the solid content, so as to provide a guarantee for the continuous work of the subsequent equipment. It has been proved that the more suitable water content after the first concentration is controlled at 85-90%, too low a water content will cause difficulties in releasing the underflow and clogging of the pipeline; too high a water content will increase the hydraulic load of the subsequent equipment and lead to the decline in operating efficiency. The sludge after primary concentration is flocculated for the second time, and then it is thickened for the second time, adopting the belt thickening method, and the water content is reduced to 70-80%. When the sludge after secondary concentration is flocculated for the third time, the flocculant is different from that of the previous two times, and the flocculating agent is different from that of the previous two times.It is like breaking up the flocs first and then flocculation again, releasing a large amount of free water wrapped up in the concentrated flocs to meet the requirements of high intensity operation of dewatering immediately after the filter press and realise high effective dewatering efficiency. The sludge is pressed by the high-pressure belt dewatering machine into solids with a water content of ≤50%.
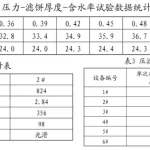
3 Compound chemical process application system operation effect According to the current domestic winch suction dredging volume, 8 inch winch suction dredging volume per hour for the underwater side of 60 ~ 100 m3, a single set of units per hour to deal with the absolute dry sludge volume of 15 ~ 30 t per hour can be dewatered sludge volume of 20 ~ 40 m3. The composite chemical process is applied in the dredging and curing project of Meishe River in Haikou City, Hainan Province, and the width of the equipment is controlled to be within 3 m. The pumping capacity of a single set of system is 15 to 30 t per hour. A single set of system hourly pumped into the slurry volume of 200-500 m (rated value of 3,350 m3), after the rubbish sand and gravel sorting, the slurry water content ≥ 95%, through the conditioning and flocculation into the thickener tower, the first concentration of the hourly discharge of 150 m3 of sludge, the range of water content in the 85-90%, the hourly discharge of clear water volume of 100-300 m3. After the second flocculation, the sludge enters the belt thickener, and after the second flocculation, the sludge is discharged 50-80 m3 per hour, and the water content is in the range of 70-80%. The sludge enters the high-pressure filter belt dewatering machine after the last flocculation, and after the dewatering, the sludge cake discharged is about 20-40 m3 per hour, and the water content can be reduced to the lowest value. Table 1 shows the results of the two experiments with a total of 350 m3 of slurry pumped per hour. The water content of the sludge becomes lower after each concentration dewatering process, and the final cake formed by filter press dewatering has a water content of less than 50%, which is in line with the requirements of sludge treatment for reduction and resourcing, and shows that the chemical process is feasible.
 Plate and frame chamber diaphragm filter presses
Plate and frame chamber diaphragm filter presses